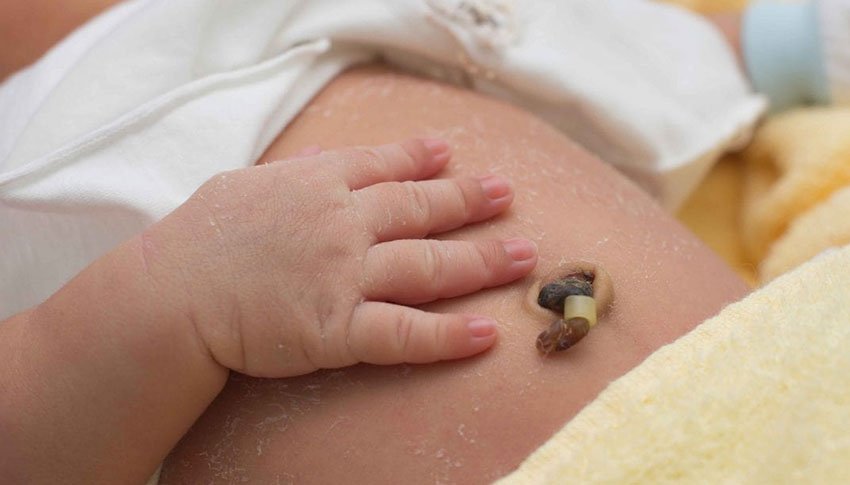
The use of an antiseptic reduces umbilical cord infection and associated neonatal death.
The use of a topical antiseptic to clean the umbilical cord in newborns and infants significantly reduces the risk of infection and neonatal mortality. More than 3 million children die each year worldwide, with infections causing approximately one third of all neonatal deaths. The greatest risk of infection occurs in those countries where the majority of deliveries take place in homes, usually attended in poor conditions.
Two studies, conducted in rural areas of Pakistan and Bangladesh, compared the use of an antiseptic, hand washing and dry cord care (in which the umbilical cord is allowed to dry without any treatment).
The results, published in the journal The Lancet, show that a simple and inexpensive measure, such as cleaning the umbilical cord with chlorhexidine, prevents infection of the umbilical cord, and therefore reduces neonatal deaths by up to 38%.